The Financial Health Checklist for Mid Market and SMEs

Understanding and improving the financial health of your business is not just a task—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re a business owner, manager, or entrepreneur, your company’s financial performance forms the backbone of strategic decision-making. A comprehensive financial health checkup allows you to identify strengths, weaknesses, and identify areas which you have to align your financial operations with your business goals. In a nutshell, it’s a paramount tool to start working “On the business” instead of “In the business”.
This article provides a detailed guide on conducting a financial health checkup, focusing on cash flow management, profit margins, debt levels, cost optimization, and critical financial ratios. With actionable steps, you’ll gain the clarity needed to secure your business’s future.
Consider these eye-opening statistics:
60% of Canadian small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) struggle with cash flow management, with delayed invoicing and payments (30%) and challenges managing accounts receivable and payable (26%) as the most common issues.
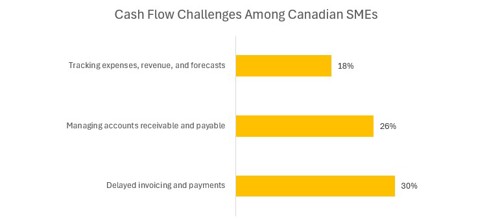
Alarmingly, 18% of businesses report difficulties in tracking expenses, revenue, and creating accurate forecasts, often due to a lack of automation and modern tools.
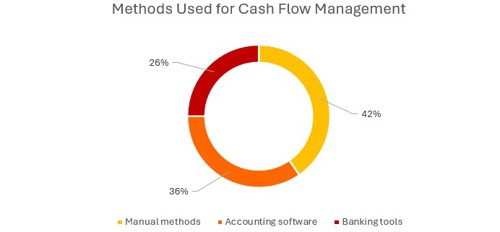
As you can see the below chart, with 42% of SMEs still managing cash flow using spreadsheets or paper records. By contrast, only 36% use accounting software, and just 26% leverage banking tools.
Industries such as manufacturing face the brunt of these issues, with 83% reporting cash flow challenges. Meanwhile, smaller businesses and professional services firms are less likely to recognize the importance of improving cash flow efficiency, despite evidence that digital tools can automate manual, time-intensive tasks.
Accounts receivable mismanagement may also trigger cash flow issues. When examining many small businesses’ billing practices, these high figures in outstanding receivables begin to make sense. For example, more than half of small businesses globally (53%) bill customers for goods/services on a specific date, compared to 47% that utilize advanced payment – charging customers for goods/services before or at the time of receiving them. Furthermore, nearly two thirds (66%) of small business owners report that the time it takes the money to process after receiving a payment has the largest impact on their company’s cash flow, compared to not getting paid by customers or clients within the terms of the payment system (34%). Finally, nearly a third of small businesses (31%) estimate it takes more than 30 days to get paid, by customers, clients, vendors or banks. During this month of lag businesses still need to cover expenses including overhead and labor costs – thus creating cash flow woes.
So, what other factors are driving cash flow problems for SMEs?
It is not only the receivables/payables mismanagement that causes cash flow issues in SMEs but also inventory mismanagement is a potential driver of these issues. Slow-moving inventory or mismanagement ties up capital that SMEs need for essential expenses like paying suppliers, employees, or loans. Unsold inventory increases holding costs, risks obsolescence, and may require discounts or write-offs, directly impacting profitability. Overstocking further locks up funds, while stockouts lead to lost sales and damaged customer relationships. These issues strain cash flow, delay supplier payments, and reduce access to credit, leaving SMEs unable to meet financial obligations or invest in growth.
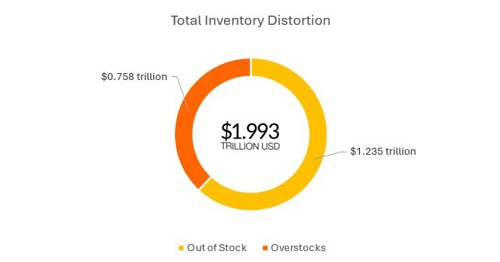
Another significant factor contributing to cash management problems is the inability of SMEs to effectively control their capital structure and debt levels.
A significant contributor to cash flow challenges among Canadian SMEs is their mounting debt load. As of Q1 2024, the total balance of loans extended to businesses hit $31.9 billion, a 7.4% increase from the previous year. The residual debt from programs like CEBA has led many SMEs to rely on installment loans, with new loan issuance up 74% year-over-year in the second half of 2023. As a result, businesses, particularly in sectors like retail and transportation, are facing higher delinquency rates, with some businesses missing critical payments.
Controlling debt levels is crucial for SMEs because excessive debt can lead to high interest costs, reducing available cash flow for daily operations. Unchecked borrowing may also result in over-leverage, making it difficult to meet repayment obligations during periods of reduced revenue. This financial strain can limit a business's ability to invest in growth opportunities, maintain liquidity, or weather economic downturns. Moreover, a poorly managed debt load can harm creditworthiness, making it harder to secure future financing on favorable terms. Maintaining a balanced capital structure allows SMEs to manage risks, optimize cash flow, and build resilience in an increasingly competitive market.
These challenges emphasize the importance of regular financial health checkups for SMEs. By proactively managing cash flow, receivables, inventory, and debt, businesses can enhance stability, mitigate risks, and position themselves for sustainable growth in a competitive market.
What Is a Financial Health Checkup?
A financial health checkup is a deep evaluation of your business’s financial processes, practices, and metrics. Think of it as a diagnostic tool to assess budgeting, cash flow, debts, savings, investments, and overall financial goals. This checkup ensures your financial operations align with your growth objectives, enhance operational efficiency, and safeguard assets.
For instance, if your analysis reveals that your cash flow is misaligned with your business objectives, it signals an urgent need for corrective action. Similarly, if profitability metrics are under performing, targeted strategies can help turn things around.
How to Conduct a Financial Health Checkup
Conducting a financial health checkup involves multiple steps, each offering critical insights into different aspects of your business’s financial well-being.
Step 1: Analyze Financial Statements
Financial statements are the foundation of any financial health assessment. They provide a snapshot of your business’s performance and financial position.
Income Statement:
The income statement reveals your profitability by detailing revenues, expenses, and net income over a specific period. Regularly reviewing this document helps identify trends in revenue growth or cost overruns.
Balance Sheet:
This statement outlines your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular moment in time. A strong balance sheet indicates healthy liquidity and manageable debt levels.
Cash Flow Statement:
The cash flow statement tracks the inflow and outflow of cash, categorizing them into operating, investing, and financing activities. A positive cash flow ensures you can meet short-term obligations and fund future growth.
By comparing these statements, you can evaluate your business’s financial trajectory and identify potential risks or opportunities.
Step 2: Calculate and Interpret Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are invaluable for interpreting raw data from financial statements. They allow you to measure liquidity, profitability, solvency, and efficiency with precision.
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios assess your business's ability to cover short-term obligations, ensuring smooth operations. Liquidity ratios include current ratio and quick ratio.
Profitability Ratios
Profitability ratios highlight how effectively your business generates profit from its resources. Profitability ratios include gross profit, net profit, and operating profit margins.
Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios measure your long-term financial stability and ability to meet obligations. Solvency ratios include debt-to-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios analyze how well your company utilizes resources to generate income. Efficiency ratios include inventory, receivables, and payable turnover ratios.
Step 3: Monitor Cash Flow
Cash flow is the lifeblood of your business. As Warren Buffet said: “small hole can drown a big ship”. Even profitable companies can fail without adequate liquidity. Regularly review your cash inflow and outflow patterns to identify potential bottlenecks.
For example, a company with rising accounts receivable but declining cash flow may need to tighten credit policies or improve collection practices.
Step 4: Assess Budgeting and Forecasting Practices
Effective budgeting and forecasting are cornerstones of financial health. A well-structured budget helps allocate resources effectively, while forecasts provide insights into future financial performance.
By comparing actual results to projections, you can identify gaps, refine your budgeting processes, and prepare for unexpected challenges.
Step 5: Evaluate Asset Utilization
Analyzing how efficiently your business uses its assets to generate revenue is critical. Metrics like return on assets (ROA) and asset turnover ratios help determine whether your resources are being maximized.
Takeaway
Conducting a thorough financial health checkup, supported by a clear understanding of financial ratios, equips you to make informed decisions and drive sustainable growth. By regularly analyzing key metrics, monitoring cash flow, and leveraging insights from financial statements, your business can stay ahead of challenges and seize opportunities.
Contact Details:
Phone: 403-375-9955
Email: info@pkfantares.com